WP6-21: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "== Introduction == ACORDE IPS was motivated by the specific positioning needs and requirements for a drone flying on an large indoor scenario. The need for considering different requirements, several aspects and levels of a Cyber-physical system (tunnel geometry, deployment of anchors, algorithms for 3D positioning, platform limitations, interfaces) made early evident that a more holistic, model-based design was necessary. It motivated the development of the IPS Modell...") |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
That is, IPS-MAF enables a holistic model of the IPS, while integrating some actual pieces of the application, so in that sense it also enables to advance some part of the application development. Therefore IPS-MAF feeds the conventional platform development and embedded application development phases, where ACORDE has already long expertise. At the same time, the measurements and characterizations that can be derived and refined from platform and application development serve to feedback and polish the holistic model. Summing up, an extended system-level design flow has been enabled, after coupling IPS-MAF to conventional ACORDE development processes for platform development (which includes PCB design, mechanical design, drivers’ development, embedded application development) and application development (where ACORDE typically develops in C or C++, relying on some cross-development environment suited to a specific microcontroller). | That is, IPS-MAF enables a holistic model of the IPS, while integrating some actual pieces of the application, so in that sense it also enables to advance some part of the application development. Therefore IPS-MAF feeds the conventional platform development and embedded application development phases, where ACORDE has already long expertise. At the same time, the measurements and characterizations that can be derived and refined from platform and application development serve to feedback and polish the holistic model. Summing up, an extended system-level design flow has been enabled, after coupling IPS-MAF to conventional ACORDE development processes for platform development (which includes PCB design, mechanical design, drivers’ development, embedded application development) and application development (where ACORDE typically develops in C or C++, relying on some cross-development environment suited to a specific microcontroller). | ||
== Architecture == | |||
Following figure sketches the main architecture of IPS-MAF. | |||
FIGURE | |||
== Status after C4D (and some demo videos) == | |||
IPS-MAF is related to the ACORDE IPS, and its development has been triggered and done in the frame of/thanks to COMP4DRONES. | |||
After such a development, IPS-MAF provides a set of key features relevant for the design and development of IPS solutions, and specifically for large indoor infrastructures. | |||
Revision as of 10:18, 14 October 2022
Introduction
ACORDE IPS was motivated by the specific positioning needs and requirements for a drone flying on an large indoor scenario. The need for considering different requirements, several aspects and levels of a Cyber-physical system (tunnel geometry, deployment of anchors, algorithms for 3D positioning, platform limitations, interfaces) made early evident that a more holistic, model-based design was necessary. It motivated the development of the IPS Modelling and Analysis Framework (IPS-MAF), which, as shown in the figure below, can be used from early design stages, to build up a holistic model of the IPS system. IPS-MAF can be used to analyse and decide key aspect at different levels of the indoor positioning system (deployment of the anchors, sensitivities and transmission powers, transmission frequencies, etc) while keeping a holistic view of the system.
That is, IPS-MAF enables a holistic model of the IPS, while integrating some actual pieces of the application, so in that sense it also enables to advance some part of the application development. Therefore IPS-MAF feeds the conventional platform development and embedded application development phases, where ACORDE has already long expertise. At the same time, the measurements and characterizations that can be derived and refined from platform and application development serve to feedback and polish the holistic model. Summing up, an extended system-level design flow has been enabled, after coupling IPS-MAF to conventional ACORDE development processes for platform development (which includes PCB design, mechanical design, drivers’ development, embedded application development) and application development (where ACORDE typically develops in C or C++, relying on some cross-development environment suited to a specific microcontroller).
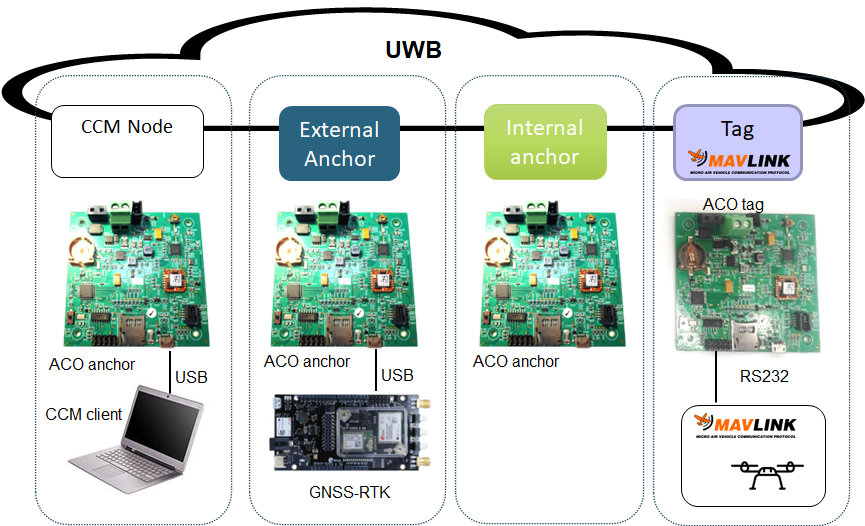
Architecture
Following figure sketches the main architecture of IPS-MAF.
FIGURE
Status after C4D (and some demo videos)
IPS-MAF is related to the ACORDE IPS, and its development has been triggered and done in the frame of/thanks to COMP4DRONES.
After such a development, IPS-MAF provides a set of key features relevant for the design and development of IPS solutions, and specifically for large indoor infrastructures.