WP6-ESDE: Difference between revisions
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
* High translation effort from the high-level model (in Matlab) to the implementation language. | * High translation effort from the high-level model (in Matlab) to the implementation language. | ||
== | ==Contribution and Improvements== | ||
The ESL embedded Software Design Environment (ESDE) of ACORDE proposes a | |||
Some key aspects of the ESDE flow for productivity improvement are: | Some key aspects of the ESDE flow for productivity improvement are: | ||
* | * Building fast especifications/models, able to capture key concerns of the application (modularity, concurrency, time model) under a unified and standard language (SystemC). | ||
* | * Executable specifications, able to significantly speed-up functional validation vs Matlab model execution. | ||
* The possibility to | * Automated embedded software generation mechanisms that avoid a significant translation effort from the system model to the implementation C/C++ code. | ||
* The possibility to validate firmware (without availability of the physical platform), | * The possibility to develop the firmware with HW development, by relying on a virtual platform. | ||
* The possibility to validate the firmware (without availability of the physical platform), or a very close version to final production firmware, on top of the virtual platform | |||
== Detailed Description == | |||
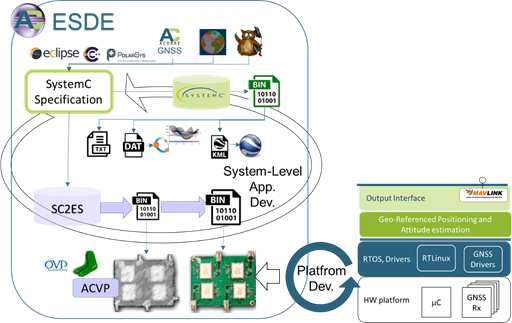
A bit more detailed description of the ESDE framework developed by ACORDE in COMP4DRONES, is sketched in the following picture. | |||
[[File:wp3-15_2_05.png|frame|center| System-level methodology for the design and implementation of outdoor geo-referenced position&attitude estimation systems in COMP4DRONES]] | |||
==Current Status (Demo) == | ==Current Status (Demo) == | ||
In C4D the tool has been further developped to support the especification a core functionality for attitude estimation (multi-baseline attitude estimation), in SystemC, i.e., which can be easily compiled into an executable model for its validation. | In C4D the tool has been further developped to support the especification a core functionality for attitude estimation (a multi-baseline attitude estimation or mbattes), in SystemC, i.e., which can be easily compiled into an executable model for its validation. | ||
See https://youtu.be/qkNS-dlBnR0 | (See https://youtu.be/qkNS-dlBnR0) | ||
Moreover, ESDE allows the targeting of this SystemC specification onto C++ based implementation, which can be automatically produced to different targets. | Moreover, ESDE allows the targeting of this SystemC specification onto C++ based implementation, which can be automatically produced to different targets. | ||
The targetting to a Linux-based platform supporting posix threads is illustrated on the following | The targetting to a Linux-based platform supporting posix threads is illustrated on the following video, where the targeting of the mbattes SystemC specification is targeted to a Linux-based target, to generate an implementation (executable file), which is launched on a PC | ||
(See ) | |||
In an additional clip, the final result of the execution shows the correctness of the implementation. | |||
== Interoperability == | |||
ESDE models are written in standard SystemC. | |||
The implementations target standard C++. For implementing RTOS services, it currently uses either POSIX API or FreeRTOS API. | |||
System-Level application models relie on modules, channels, processes elements, which facilitates mapping with other C4D frameworks, like S3D. This has been tested for the mbattes example in a collaboration between ACORDE and the University of Cantabria. | |||
Revision as of 22:12, 28 September 2022
ESL embedded Software Design Environment (ESDE)
| ID | WP6-ESDE |
| Contributor | ACORDE |
| Levels | Tool, Platform |
| Require | Linux, Virtual Platform Development Platform |
| Provide | Executable System-Level modelling, automated embedded software generation, Virtual Platform based validation |
| Input | SystemC models, RTOS API target, Platform target, Platform model |
| Output | Functional and time performance validation. Close to production firmware generation and validation. |
| C4D tooling | n.a. |
| TRL | 4 |
For the design and development of a complete positioning and attitude solution like GLAD, ACORDE relied on a conventional design flow where a former hih-level model using Matlab was used. Then a manual translation was done to C++, which was tested on the final physical prototype. While proven, this approach had also some important disadvantages:
- Enforces a sequential HW/SW development. HW/SW platform availability is a pre-condition for application development.
- Long simulation times and lacks on the modelling language (e.g., no time modelling)
- High translation effort from the high-level model (in Matlab) to the implementation language.
Contribution and Improvements
The ESL embedded Software Design Environment (ESDE) of ACORDE proposes a
Some key aspects of the ESDE flow for productivity improvement are:
- Building fast especifications/models, able to capture key concerns of the application (modularity, concurrency, time model) under a unified and standard language (SystemC).
- Executable specifications, able to significantly speed-up functional validation vs Matlab model execution.
- Automated embedded software generation mechanisms that avoid a significant translation effort from the system model to the implementation C/C++ code.
- The possibility to develop the firmware with HW development, by relying on a virtual platform.
- The possibility to validate the firmware (without availability of the physical platform), or a very close version to final production firmware, on top of the virtual platform
Detailed Description
A bit more detailed description of the ESDE framework developed by ACORDE in COMP4DRONES, is sketched in the following picture.
Current Status (Demo)
In C4D the tool has been further developped to support the especification a core functionality for attitude estimation (a multi-baseline attitude estimation or mbattes), in SystemC, i.e., which can be easily compiled into an executable model for its validation.
(See https://youtu.be/qkNS-dlBnR0)
Moreover, ESDE allows the targeting of this SystemC specification onto C++ based implementation, which can be automatically produced to different targets. The targetting to a Linux-based platform supporting posix threads is illustrated on the following video, where the targeting of the mbattes SystemC specification is targeted to a Linux-based target, to generate an implementation (executable file), which is launched on a PC
(See )
In an additional clip, the final result of the execution shows the correctness of the implementation.
Interoperability
ESDE models are written in standard SystemC. The implementations target standard C++. For implementing RTOS services, it currently uses either POSIX API or FreeRTOS API.
System-Level application models relie on modules, channels, processes elements, which facilitates mapping with other C4D frameworks, like S3D. This has been tested for the mbattes example in a collaboration between ACORDE and the University of Cantabria.