WP6-ESDE
ESL embedded Software Design Environment (ESDE)
| ID | WP6-ESDE |
| Contributor | ACORDE |
| Levels | Tool, Platform |
| Require | Linux, Virtual Platform Development Platform |
| Provide | Executable System-Level modelling, automated embedded software generation, Virtual Platform based validation |
| Input | SystemC models, RTOS API target, Platform target, Platform model |
| Output | Functional and time performance validation. Close to production firmware generation and validation. |
| C4D tooling | n.a. |
| TRL | 4 |
For the design and development of a complete positioning and attitude solution like GLAD, ACORDE relied on a conventional design flow where a former hih-level model using Matlab was used. Then a manual translation was done to C++, which was tested on the final physical prototype. While proven, this approach had also some important disadvantages:
- Enforces a sequential HW/SW development. HW/SW platform availability is a pre-condition for application development.
- Long simulation times and lacks on the modelling language (e.g., no time modelling)
- High translation effort from the high-level model (in Matlab) to the implementation language.
Detailed Description
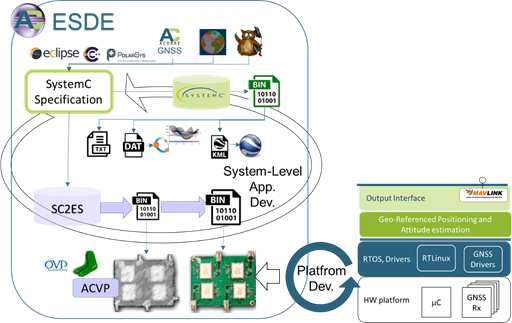
In COMP4DRONES, ACORDE is developing and evaluating a newer approach to overcome those drawbacks. It is sketched in Figure 69. The ESDE framework developed in WP6 [33], is encrusted in at a top level layer, for a system-level approach to embedded software design and development, to encompass the conventional HW/SW platform development capabilities and processes of ACORDE.
Contribution and Improvements
Some key aspects of the ESDE flow for productivity improvement are:
- The fast functional models that can be built at the top lever, able to significantly speed-up functional validation vs Matlab model execution.
- The automated embedded software generation mechanisms that avoid a significant translation effort from the system model to the implementation C/C++ code.
- The possibility to parallelize of the development of firmware (binary or object file), or very close version of it with HW development, by relying on a high-fidelity virtual platform.
- The possibility to validate firmware (without availability of the physical platform), eventually using several virtual platforms for test parallelization
Interoperability with other C4D tools
TBC